




Next: Uncorrecting Images: uncorrect
Up: Performing Image Correction: corr_im_fast
Previous: What corr_im_fast Does
Contents
Index
This is a short description of the steps that new_dfc takes.
- new_dfc must be provided with the image, output file, flat, dark,
fringe map, and thumbnail file names.
- The program first subtracts the dark frame from the image.
- It next divides the image by the flat-field image to remove vignetting
and account for interpixel sensitivity variations.
- It next scales the fringe map as described in
Section 7.3.4, and subtracts the scaled fringe map.
If the fringe map fit is considered to be ``bad,'' (the
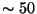 ), then the fringe map is not subtracted and this is noted in the
FITS header. (See Section C.2.)
), then the fringe map is not subtracted and this is noted in the
FITS header. (See Section C.2.)
- It next crops the image as defined on the command line. The cropping
algorithm is flexible enough to handle a central bias region that results from
dual-amplifier readout.
- The program now ``compresses'' the image with the FITS standard b-zero
and b-scale parameters, to change the image from a 32-bit floating point image
to a compressed 16-bit integer image, as described in Appendix B.1.
- A thumbnail jpeg image is created for easy display on the web page. The
typical thumbnail is 8 k.
- The program exits and returns to corr_im_fast.
All the operations performed to correct an image are recorded in the FITS
header. It will soon be possible to reverse the correction process, however,
with a loss of bias region information.
For more details on running the correction software, see Chapter 8.





Next: Uncorrecting Images: uncorrect
Up: Performing Image Correction: corr_im_fast
Previous: What corr_im_fast Does
Contents
Index
Rotse Pager
2003-05-20
![]() ), then the fringe map is not subtracted and this is noted in the
FITS header. (See Section C.2.)
), then the fringe map is not subtracted and this is noted in the
FITS header. (See Section C.2.)
![]() ), then the fringe map is not subtracted and this is noted in the
FITS header. (See Section C.2.)
), then the fringe map is not subtracted and this is noted in the
FITS header. (See Section C.2.)